Fetch
The Fetch API is a built-in feature in modern browsers that allows you to make web requests. It operates asynchronously and uses promises to simplify response handling. By default, the fetch function takes a URL as its first argument and sends an HTTP GET request if not specified otherwise.
fetch('https://mydomain.com/api')
.then(response => {
// Handle response
})
.catch(err => {
// Something went wrong
});
You can extract the JSON payload from a successful request by using the json() method.
fetch('https://mydomain.com/api')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
// Handle data
})
.catch(err => {
// Something went wrong
});
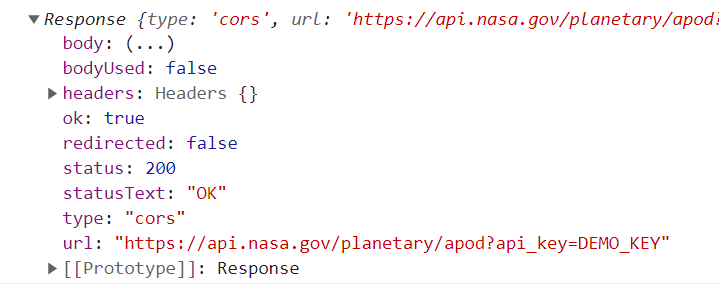
Response
The response is an object that contains properties such as body, headers, status, etc. (https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Response)
fetch('https://mydomain.com/api')
.then(response => console.log(response))
Setting HTTP method & headers
You can also pass a second argument to fetch function that is an optional object containing options to configure the request. You can use the method property to specify different HTTP request methods. Request headers provide the server with additional information about the request, such as the format of the request body. The headers property can be used to set these request headers.
The request body is the payload of the request, for example, the data that the client is sending to the server. To set the request body, you can use the body property.
fetch('https://mydomain.com/api', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Accept': 'application/json',
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({ message: 'Hello World!' })
})
.then(response => {
// Handle response
})
.catch(err => {
// Something went wrong
});
Response status
You should also check the response status. The response.ok propery returns true if the response status is 2XX.
fetch('https://mydomain.com/api')
.then(response => {
if (!response.ok)
throw new Error(response.statusText)
return response.json()
})
.then(data => {
// Handle data
})
.catch(err => {
// Something went wrong
});
async / await
In this material, we use then statements, but you can use async/await as well to handle promises.
const fetchData = async () => {
try {
const response = await fetch('https://mydomain.com/api');
const data = await response.json();
}
catch(error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
Further reading
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Fetch_API
- Axios https://axios-http.com/ Popular JavaScript library for HTTP requests.