CI Pipelines
CI workflow
In this section, we will implement simple CI workflow to lint, build and test the Node.js app.
- Fork the app from this repository.
This is a Node.js Express calculator application. You can start the app using the npm run start command. By default, it listens on port 3000. To perform calculations, send a POST request to the /calculate endpoint. The request body should include the operation (add, subtract, multiply, or divide) and two numbers (a and b). The response will return the result of the calculation.
-
Clone the forked repository to your computer.
-
Install the dependencies, start the application, and verify that it functions correctly.
-
Create
./github/workflows/ci_workflow.yamlfile
Now, we are ready to write our workflow file. First we define a name of the workflow. The event that executes workflow is push and merge a branch to the main branch:
# Node.js CI pipeline
name: Node.js CI
on:
push:
branches: [main]
pull_request:
branches: [main]
Next, we define jobs for our workflow. The jobs will be run on the latest version of ubuntu.
# Node.js CI pipeline
name: Node.js CI
on:
push:
branches: [main]
pull_request:
branches: [main]
jobs:
Node-ci-pipeline:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
Then we have to define steps for the Node-ci-pipeline job. Github provides pre-defined actions for specific purposes. Actions are pre-defined set of jobs or code that perform specific task. You can explore different actions in Github marketplace.
The checkout action is responsible for checkout your repository so that the workflow can access its contents. The setup-node action is used to configure the specified version of Node.js on the runner. The @4 indicates the version of the action being used. The with keyword allows you to define additional parameters, such as the Node.js version.
# Node.js CI pipeline
name: Node.js CI
on:
push:
branches: [main]
pull_request:
branches: [main]
jobs:
Node-ci-pipeline:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v5
- uses: actions/setup-node@v5
with:
node-version: '24'
Now, we are ready to perform linting, build, and testing. First, we will use the npm ci command to install dependencies in a clean environment. After the dependencies are installed, we will run the tests and then build the Node.js application..
# Node.js CI pipeline
name: Node.js CI
on:
push:
branches: [main]
pull_request:
branches: [main]
jobs:
Node-ci-pipeline:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v5
- uses: actions/setup-node@v5
with:
node-version: '24'
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm ci
- name: Linting
run: npm run lint
- name: Run tests
run: npm run test
- name: Build
run: npm run build
The npm ci command installs exactly what's in the lock file with no deviations. That guarantees the same dependencies across all environments. It requires that lock file exists and it removes existing node_modules folder before installation. It is faster than npm install in clean environments (CI piplines). Read more in https://docs.npmjs.com/cli/v8/commands/npm-ci
Commit changes to your local repository and push changes to Github repository. If you open the Actions tab of your repository, you should see the workflow running.
The workflow may initially fail due to issues in linting or testing.
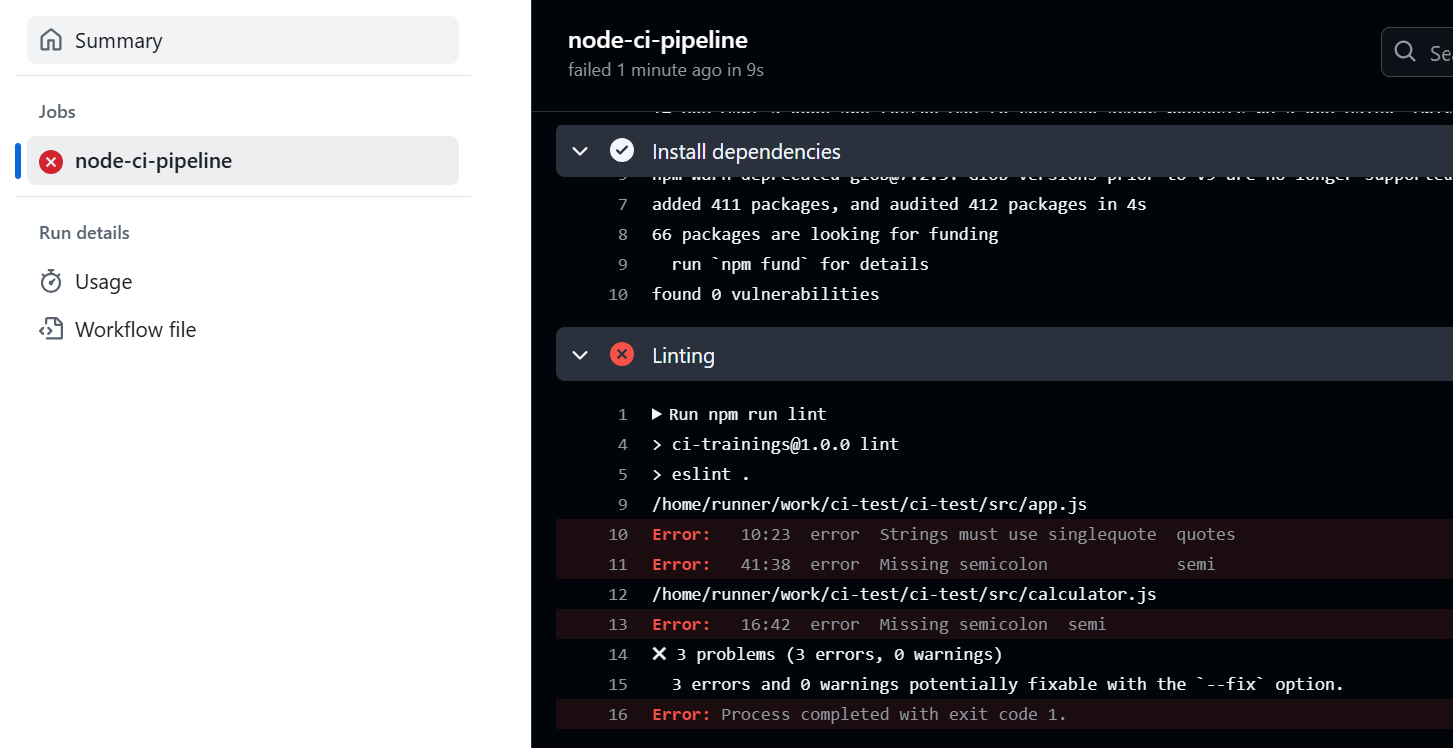
Identify and resolve these errors to ensure the workflow completes successfully with a green status.
Matrices
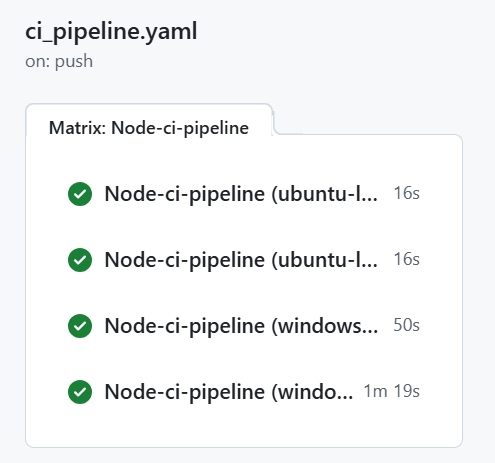
In GitHub Actions, matrices are a feature that allows you to run multiple variations of a job in parallel. This is particularly useful for testing your code across different environments, such as multiple versions of a programming language, operating systems, or configurations.
Read the matrix documentation and modify the CI workflow that we have made. The workflow should run using both the Node versions 20 and 22 and the latest ubuntu and windows versions. You should see 4 jobs executed in the workflow:
Status badge
You can display a status badge in your repository to indicate the status of your workflows. Read the instructions in the Github documentation and add a status badge to your repository.
