Context API
The Context API in React is a way to manage and share state across multiple components without the need to pass props down the component tree. It is useful for handling global or shared state, such as user authentication status, theme, or any data that multiple components need access to.
Using the props vs Context API:
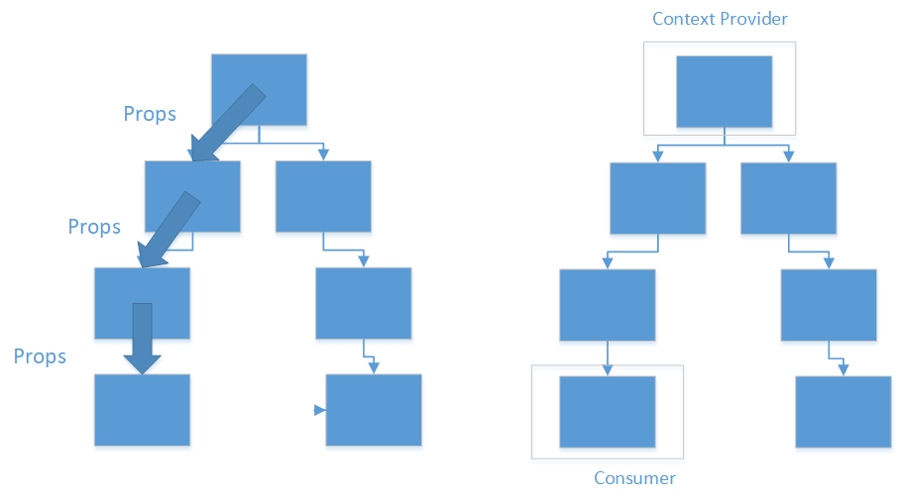
To start using context, you need to create if first. You typically define this in a separate file. The createContext is used to create a context that components can provide to read. It takes one argument that is the default value.
import { createContext } from 'react';
type Theme = "light" | "dark"
const ThemeContext = createContext<Theme>("light");
export default ThemeContext;
The createContext returns a context object that has Provider and Consumer properties. The Provider property is used to provide context value to components.
Next, we create context provider that holds the shared value. It can be used to provide value to its child components.
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import ThemeContext from './ThemeContext';
const ThemeProvider = ({ children }) => {
const [theme, setTheme] = useState("light");
const toggleTheme = () => {
setTheme((prevTheme) => (prevTheme === "light" ? "dark" : "light"));
};
return (
<ThemeContext.Provider value={{ theme, toggleTheme }}>
{children}
</ThemeContext.Provider>
);
};
export default ThemeProvider;
Now, any component within ThemeProvider can access the context usint the React useContext hook function.
import { useContext } from 'react';
import ThemeContext from './ThemeContext';
const MyComponent = () => {
const { theme, toggleTheme } = useContext(ThemeContext);
return (
<>
<button onClick={toggleTheme}>Change theme</button>
<p>Current theme is: {theme}</p>
</>
);
};
export default MyComponent;